Why omega 3 fats are helpful in boosting metabolism?
omega 3 fats
Why does eating lots of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, herring, and tuna) are helpful in boosting your metabolism?
Cod liver oil contains the most healthy omega-3.
Omega-3 s balance blood sugar and reduce inflammation, helping to regulate metabolism.
They may also reduce resistance to the hormone leptin, which researchers have linked to how fast fat is burned.
A study in Obesity Research found rats that ingested large doses of fish oil while exercising lost weight!
Take omega-3 fatty acid supplements; Hyman recommends 1,000 to 2,000 milligrams per day.
Omega 3-6-9 is a combination of well-known nutritional oils provides a unique balance of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Essential Fatty Acids plus Omega-9, a non-essential, but beneficial fatty acid. The Omega-3’s, Alpha Linolenic Acid, EPA and DHA, and the Omega-6, GLA, are necessary for the maintenance of cardiovascular, nervous system and skin health. Oleic Acid, an Omega-9, has also been shown to promote a healthy vascular system.
DXN Spirulina contains Omega 3-,6 and 9s and is especially high in Omega-3s.
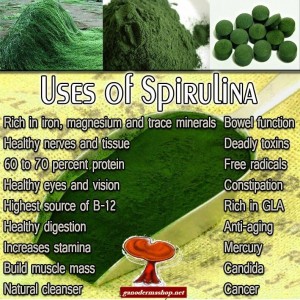
Spirulina contains Omega 3-,6 and 9s and is especially high in Omega-3s.
Spirulina is extremely high in Chlorophyll, which helps remove toxins from the blood and boost the immune system. People report feeling benefits whenever and however they take Spirulina.
Clinical evidence is strongest for heart disease and problems that contribute to heart disease, but omega-3 fatty acids may also be used for:
Omega 3 fats – Fights high cholesterol
Several studies have shown that fish oil supplements reduce triglyceride levels.
Omega 3 fats – High blood pressure
Several clinical studies suggest that diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids lower blood pressure in people with hypertension.
Omega 3 fats – Fights Heart diseases
The role of omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease is well established. One of the best ways to help prevent heart disease is to eat a diet low in saturated fat and to eat foods that are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (including omega-3 fatty acids).
Omega 3 fats – Diabetes
People with diabetes often have high triglyceride and low HDL levels. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil can help lower triglycerides and apoproteins (markers of diabetes), and raise HDL, so eating foods or taking fish oil supplements may help people with diabetes.
Omega 3 fats – Rheumatoid arthritis
A number of small studies have found that fish oil helps reduce symptoms of RA, including joint pain and morning stiffness. One study suggests that people with RA who take fish oil may be able to lower their dose of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Omega 3 fats – Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Several small studies suggest that EPA and fish oil may help reduce symptoms of lupus, an autoimmune condition characterized by fatigue and joint pain. However, 2 small studies found fish oil had no effect on lupus nephritis (kidney disease caused by lupus, a frequent complication of the disease).
Omega 3 fats – Osteoporosis
Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may help increase levels of calcium in the body and improve bone strength, although not all results were positive. Some studies also suggest that people who don’t get enough of some essential fatty acids (particularly EPA and gamma-linolenic acid [GLA], an omega-6 fatty acid) are more likely to have bone loss than those with normal levels of these fatty acids.
Omega 3 fats – Depression
Studies have found mixed results as to whether taking omega-3 fatty acids can help depression symptoms.
Omega 3 fats – Bipolar disorder
In a clinical study of 30 people with bipolar disorder, those who took fish oil in addition to standard prescription treatments for bipolar disorder for 4 months experienced fewer mood swings and relapse than those who received placebo.
Omega 3 fats – Schizophrenia
Preliminary clinical evidence suggests that people with schizophrenia may have an improvement in symptoms when given omega-3 fatty acids. However, a recent well designed study concluded that EPA supplements are no better than placebo in improving symptoms of this condition.
Omega 3 fats – Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may have low levels of certain essential fatty acids (including EPA and DHA). In a clinical study of nearly 100 boys, those with lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids had more learning and behavioral problems (such as temper tantrums and sleep disturbances) than boys with normal omega-3 fatty acid levels.
Omega 3 fats – Omega 3 fats – Cognitive decline
A number of studies show that reduced intake of omega-3 fatty acids is associated with increased risk of age related cognitive decline or dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease. Scientists believe the omega-3 fatty acid DHA is protective against Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
Omega 3 fats – fights skin disorders
In one clinical study, 13 people with sun sensitivity known as photo dermatitis showed less sensitivity to UV rays after taking fish oil supplements. However, topical sunscreens are much better at protecting the skin from damaging effects of the sun than omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega 3 fats – Macular Degeneration
A questionnaire given to more than 3,000 people over the age of 49 found that those who ate more fish were less likely to have macular degeneration (a serious age related eye condition that can progress to blindness) than those who ate less fish.
Omega 3 fats – Menstrual pain
In one study of 42 women, they had less menstrual pain when they took fish oil supplements than when they took placebo.
DXN Spirulina contains Omega 3-,6 and 9s and is especially high in Omega-3s.

Spirulina contains Omega 3-,6 and 9s and is especially high in Omega-3s.
Spirulina is extremely high in Chlorophyll, which helps remove toxins from the blood and boost the immune system. People report feeling benefits whenever and however they take Spirulina.
Omega 3 fats – Colon cancer
Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids seems to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
Omega 3 fats – Breast cancer
Although not all experts agree, women who eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids over many years may be less likely to develop breast cancer.
Omega 3 fats – Prostate cancer
Population based studies of groups of men suggest that a low fat diet including omega-3 fatty acids from fish or fish oil help prevent the development of prostate cancer.
Source: Omega-3 fatty acids | University of Maryland Medical Center


